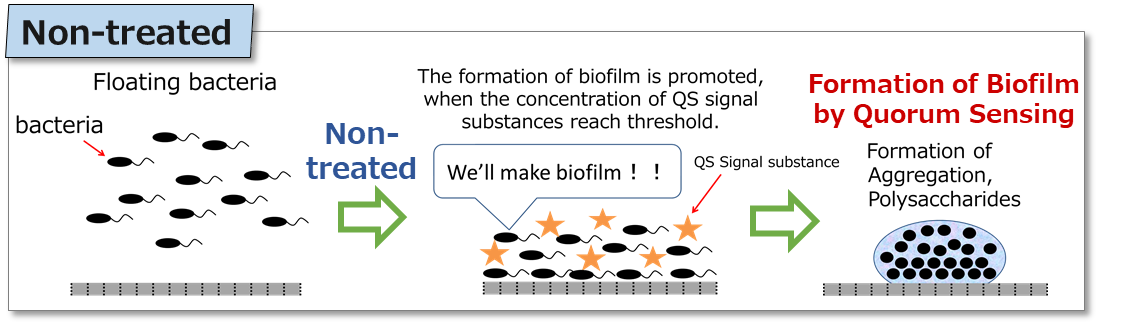
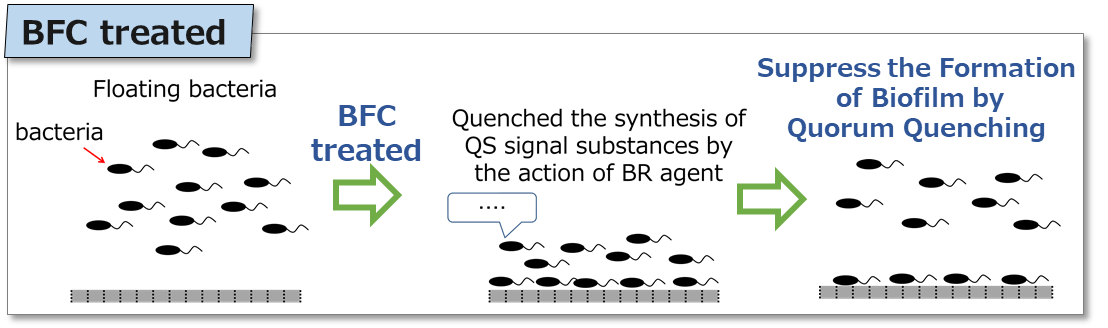
Biofilm control agent (BFC) is highly effective on inhibiting biofilm (BF) formation and on removing accumulated biofilms.
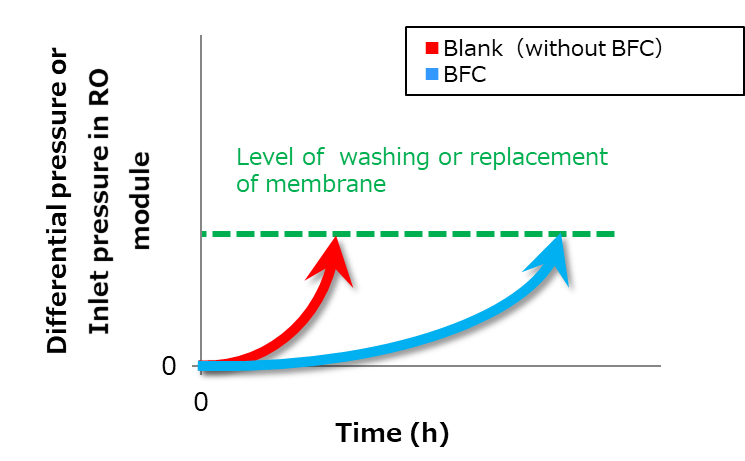
For example, the use of BFC to RO membrane can reduce biofouling (*1) and consequently reduce the frequency of washing and replacement of RO membrane.
*1. Clogging the membrane by biofilms or the other substances derived from bacterial cells
↓ Please scroll to the side to see
| term | BR-105 |
BR-108 |
BR-109
|
BR-110 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
Colorless liquid |
Light brown liquid |
Light brown liquid |
|
Mechanism of action on BF |
Inhibition of QS, detergent action |
Inhibition of QS |
Inhibition of QS |
Inhibition of QS, detergent action |
| Effect |
Inhibition of BF formation, Removal of BF |
Inhibition of BF formation |
Inhibition of BF formation |
Inhibition of BF formation, Removal of BF |
| Recommended concentration | 10% | 10 % |
0.35 % |
0.35 % |
| Freezing Temperature(°C) | -4~-2℃ | -4~-2℃ |
4~6℃ |
-2~0℃ |
| Dispersibility in water | Good | Good |
Require stir for about 5 min |
Good, but require slightly stir |
| pH | 7.0~8.0 | 6.0~8.0 |
5.8~8.0 |
6.0~7.0 |
| BR-110 |
6 months (25 °C or less) No performance deterioration due to freeze – thaw. |
6 months (25 °C or less) No performance deterioration due to freeze – thaw. |
6 months (25 °C or less) No performance deterioration due to freeze – thaw. |
Still confirming |
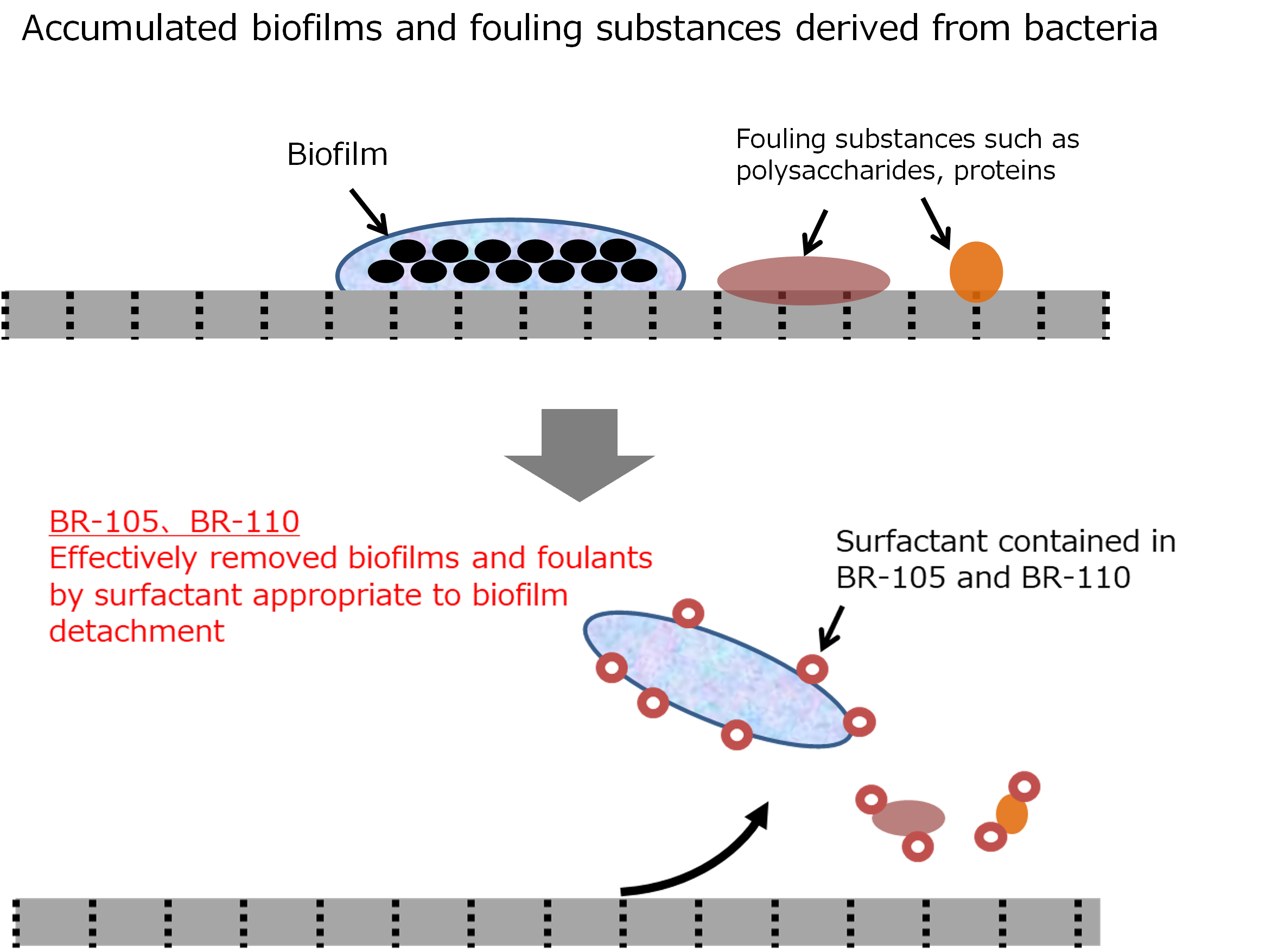
*3. Substances derived from bacteria causing membrane clogging
| BFC | |
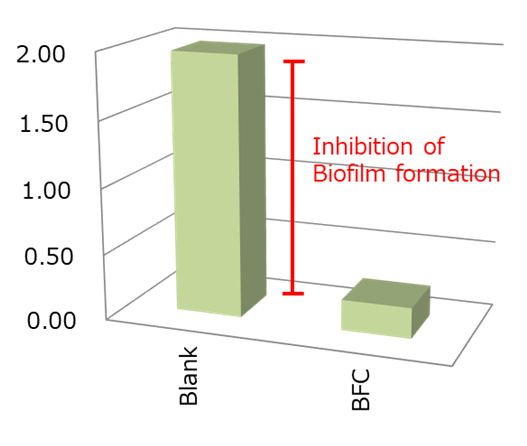
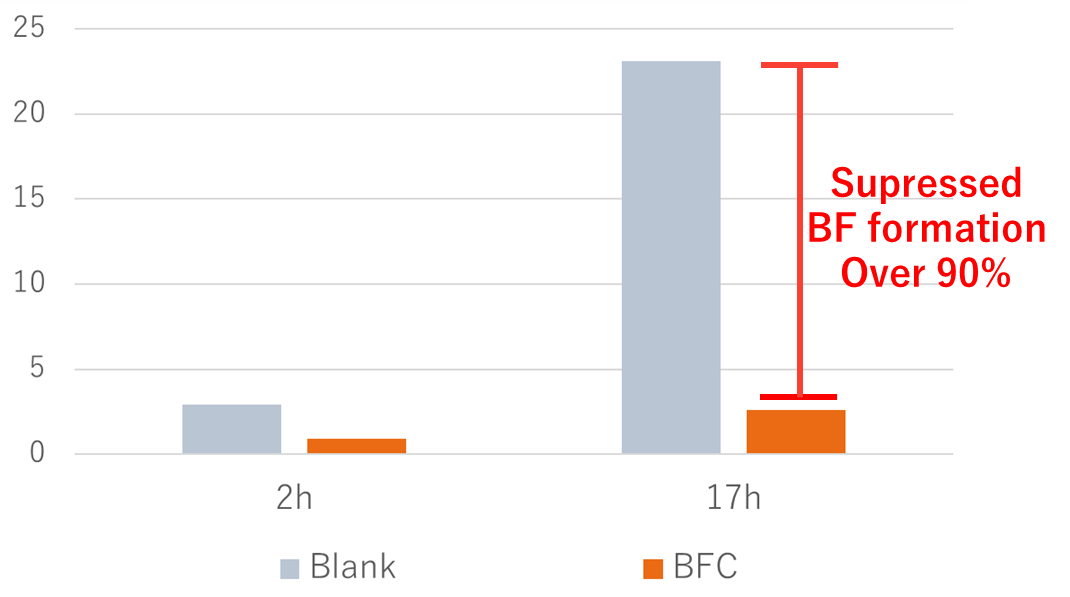
| Inhibiting rate of biofilm formation (%) | 88 |
| Viable cell number (cfu/mL) | 108 |
BF formation rate on Blank: 0%
Viable cell number on Blank: 108~9
BFC can inhibit biofilm formation on various materials such as RO membranes and silicon tubes as well as plastic plate.
・Biofilm-forming bacteria (Pseudomonas sp) were cultured in medium containing BFC.
・After incubation, the biofilm formed on RO membranes and silicon tubes were subjected to crystal violet staining.


Observation of suppression of BF formation on RO membranes using a confocal microscope.
The BFC suppress the formation of BF itself, rather than suppressing the adhesion of bacteria to the surface of various substances.
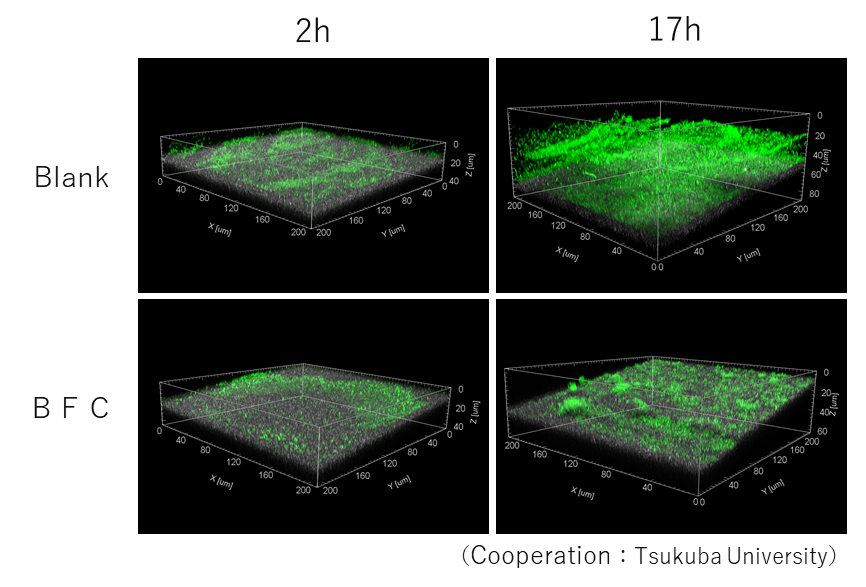
Confocal micrograph 2,17 hours after the start of BF formation.
Green fluorescence represents BF on the RO membrane surface.
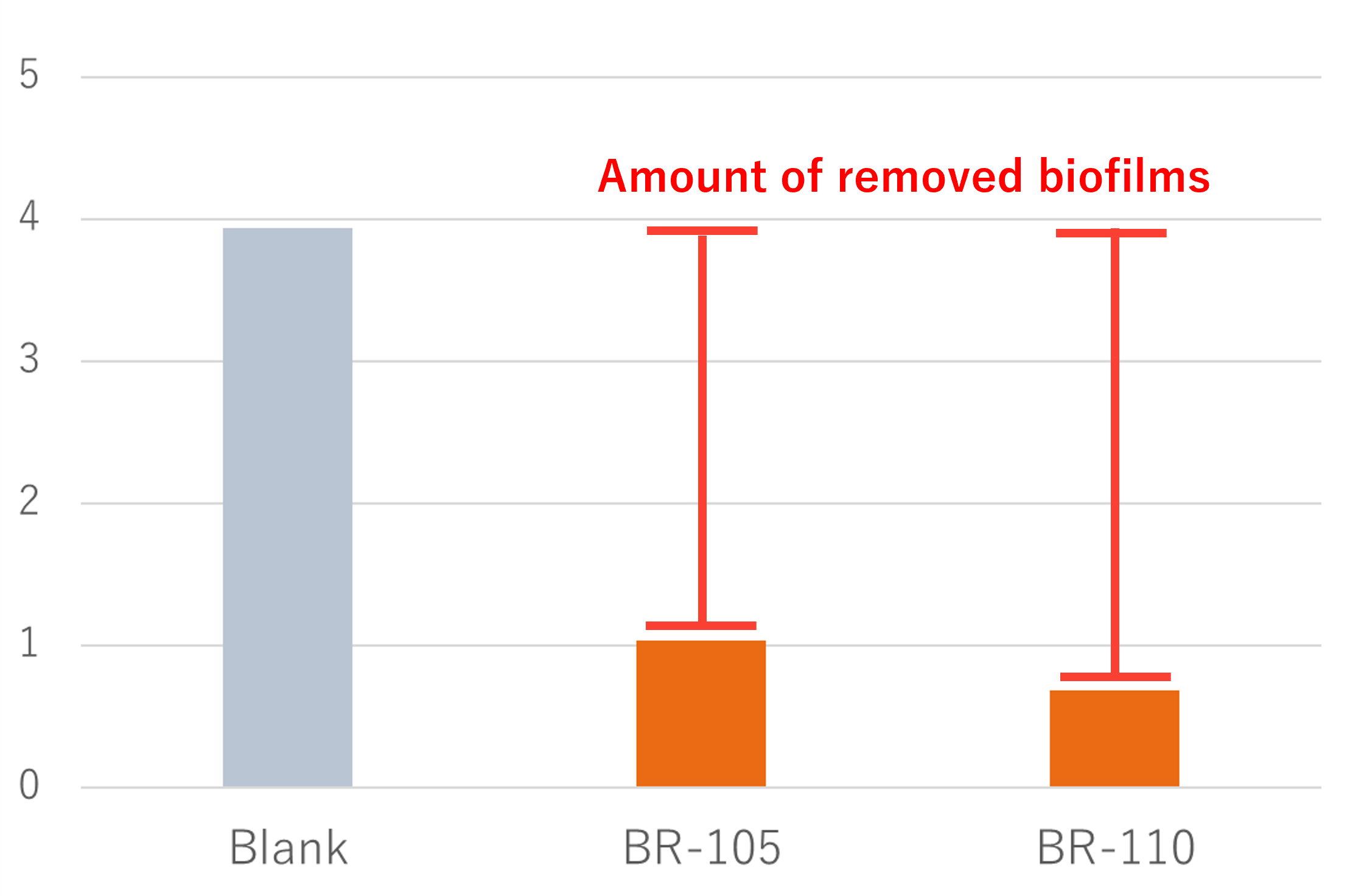
| BR-105 | BR-110 | |
| BF removal rate(%) | 74 | 83 |
BF removal rate on Blank: 0%
*4. Differences of pressure between input (feed water side) and output (concentrated wastewater side)
We are working with our clients to develop a variety of practical applications.
For further information, please contact us from inquiry form on our website.